English
繁體中文
简体中文
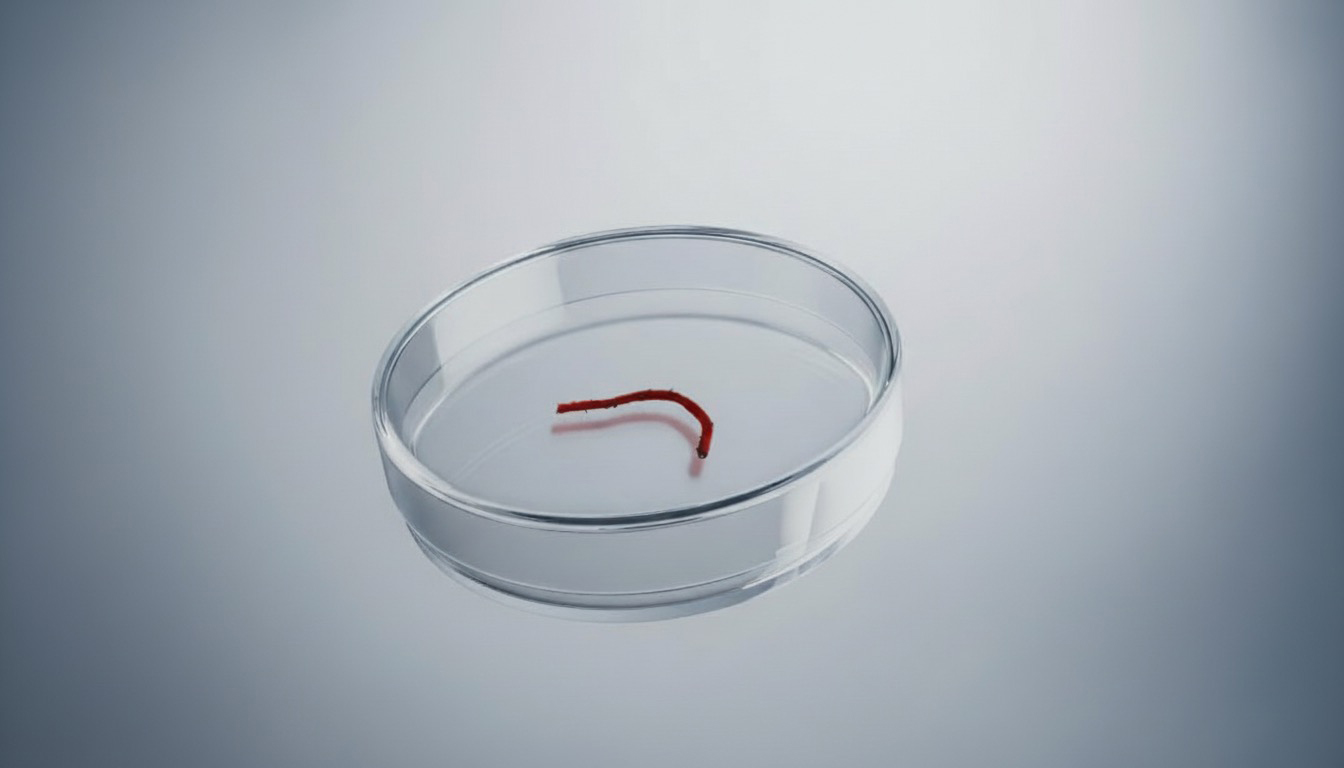

Don’t mistakenly regard this tiny wriggler as a blood worm – it is a revolutionary microrobot, crafted from a patient’s own blood cells and finer than a human hair, designed to navigate through the brain’s complex neural labyrinth with astonishing precision. Far from a sci-fi creature, CUHK’s innovative microrobots don’t just move – they slither, swim and crawl under magnetic control, hunting down cancer cells like guided missiles. Remotely steered by external magnetic fields, they deliver targeted therapy to brain tumours once considered untreatable, offering new hope where conventional methods fall short.

Pipelines are present everywhere in our daily lives – from residential plumbing and oil tanks to power plants and railway systems. Ensuring their safety is essential to prevent leaks and accidents, protect the environment, and ensure reliable delivery of vital resources. CUHK scientists are pushing the boundaries of energy innovation with smart laser sensing and AI-driven gas detection. Their breakthrough technology promises safer, smarter monitoring of oil, natural gas and hydrogen pipelines. With large-scale trials across Hong Kong and mainland China, this project fuels the city’s re-industrialisation and energy ambitions, positioning CUHK at the forefront of sustainable tech and next-generation manufacturing.
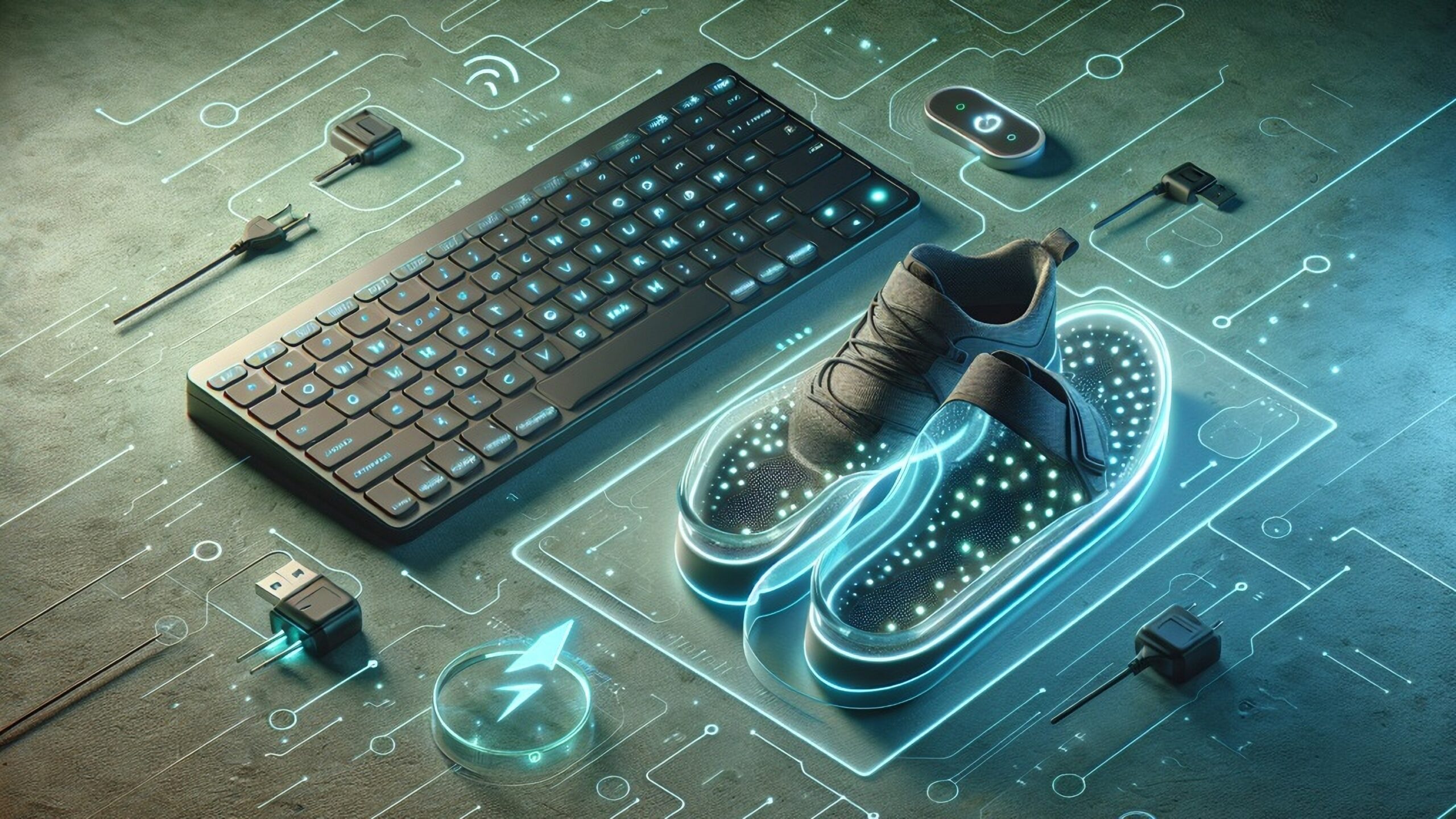

Rejoice – no more worrying about battery levels or scrambling for spares. Two CUHK inventions are bringing a battery-free future closer to reality. One powers computer keyboards using energy generated simply by pressing the keys, while the other – a smart insole – harvests energy from walking to monitor gait patterns, transforming medical diagnosis and patient care.
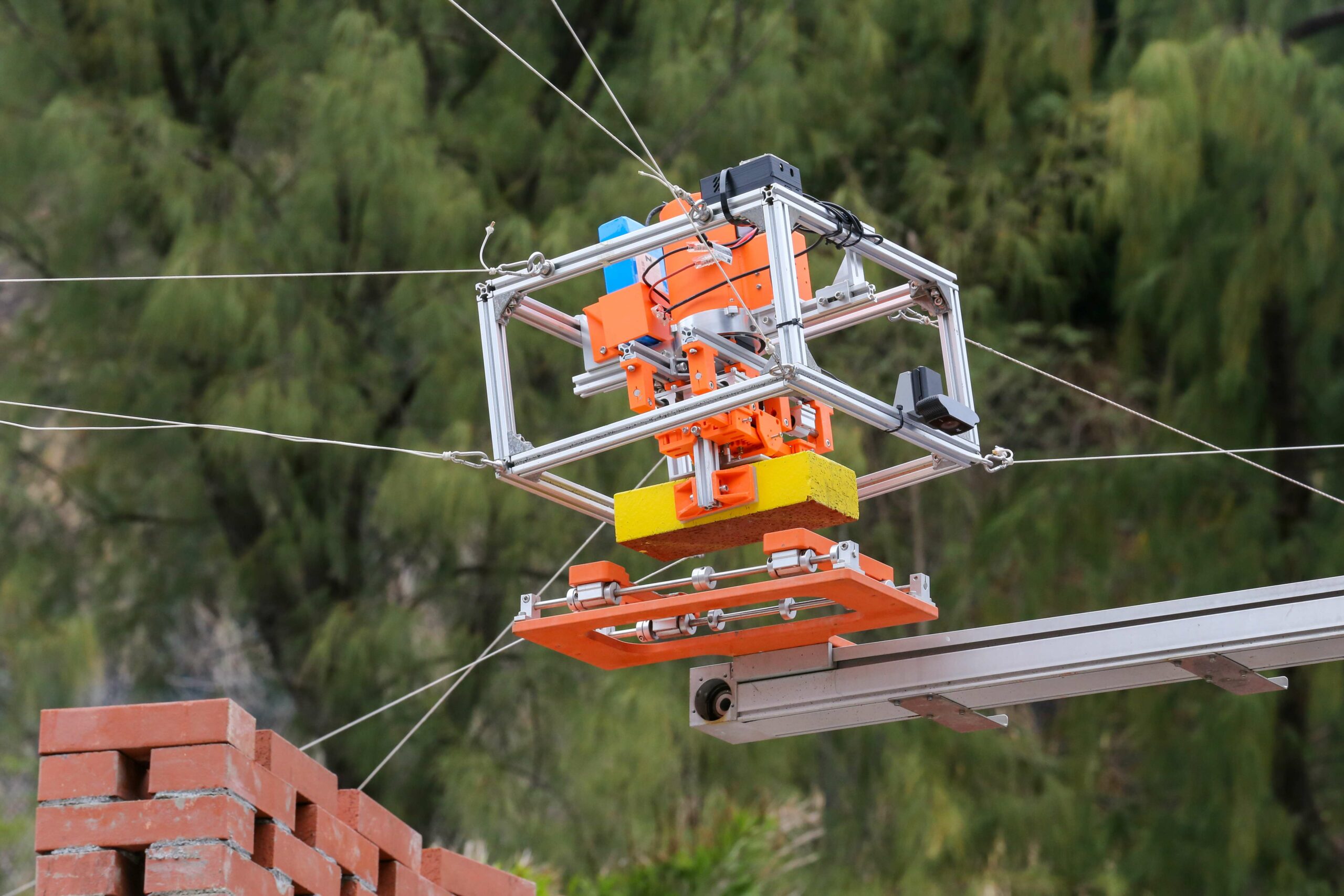

From the robust textures of the Great Wall’s ancient bricks to the meticulous assembly of Roman arches, masonry has long stood as a testament to human ingenuity and aesthetic vision. A cross-disciplinary team at CUHK has reinterpreted traditional craftsmanship through technology—CU-Brick. By integrating cable-driven robotics and automated programming, this innovation breathes new life into traditional bricklaying techniques in the digital age. The system accurately replicates the profound understanding of geometric structures mastered by historical artisans and sparks a dynamic interplay between modern engineering and creative inspiration. Bricklaying transcends mere repetitive stacking, evolving into an innovative dialogue that bridges engineering, architecture, and art—unleashing unprecedented creative potential for future architectural masterpieces.

Plants stretch toward sunlight in photosynthesis, their leaves curving to seize every beam. A CUHK team has harnessed this dance with light to shape soft, magnetic materials. Their revolutionary technology using lasers and magnets—precisely calibrating light intensity during 3D printing—transforms a flat magnetic hydrogel into a dynamic 3D surface. Beyond personalised medical patches, this breakthrough also enables human face replication, information storage, and biomimetic soft robots—all through tailored light adjustments.
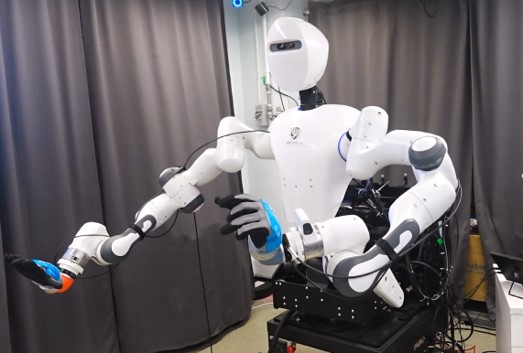
CURI, developed by CUHK, is a robot that learns tasks by observing humans. Equipped with an RGB-D camera and adaptable arms, CURI ensures precision and efficiency. The research team has used rubber pellets to simulate cooking tasks. Although CURI has not cooked real food, the potential for it to become a Michelin-star chef in the future is exciting. Imagine this Michelin-star chef can prepare perfectly seasoned dishes just for you!
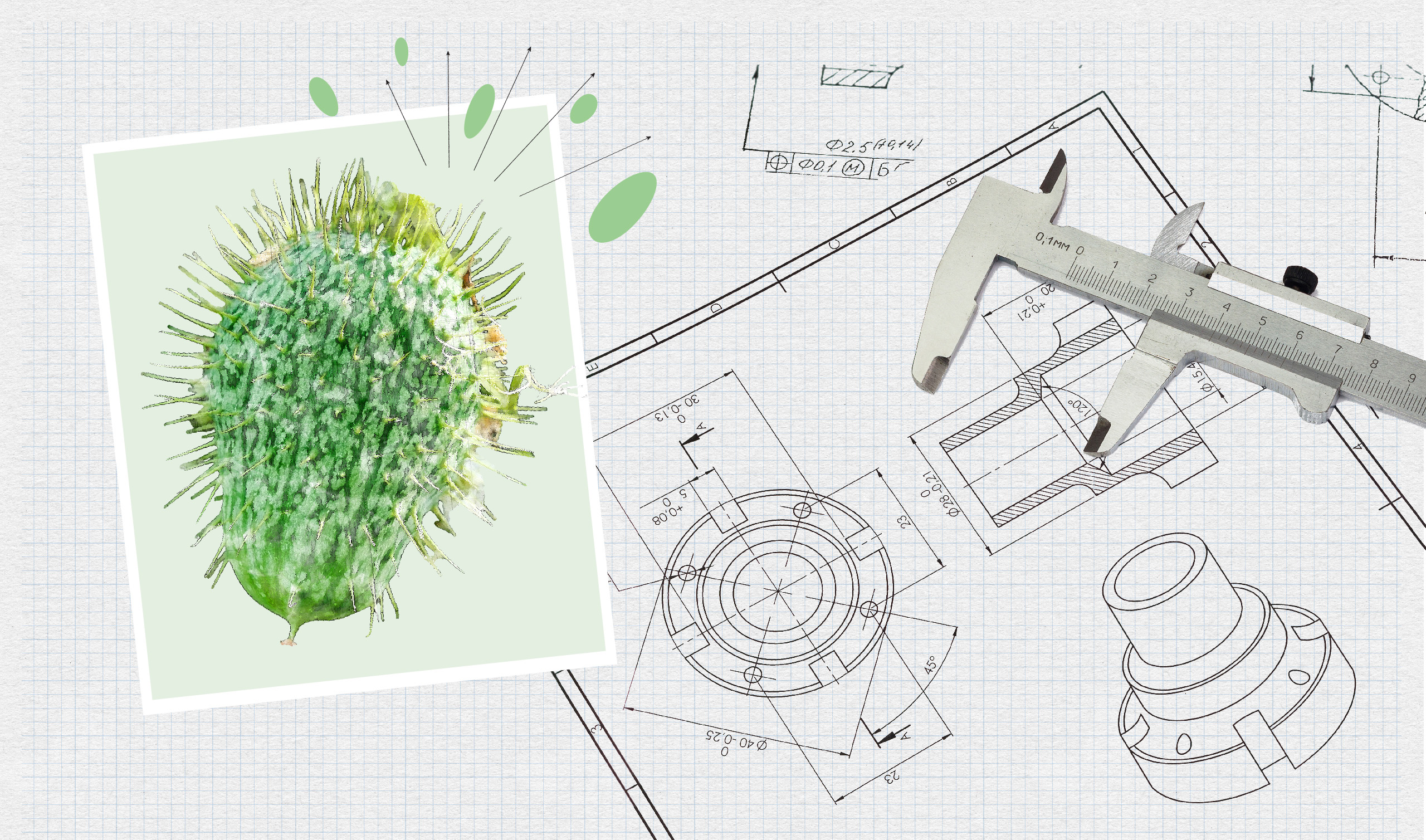
Ever seen a cucumber launch its seeds like a tiny rocket? CUHK researchers did, and they thought “Why not use that for robots?” Inspired by the squirting cucumber plant’s explosive method of launching its seeds, a CUHK research team developed a groundbreaking power amplification system that propels mini robots to new heights of speed and agility, making them perfect for medical missions deep inside the human body. With machine learning enhancing their control and navigation, these micro marvels are set to revolutionise the field of medicine.

Can you imagine how hot you would feel when a heatwave comes if you lived in a tin-sheet house? It would be like living in a steam oven. Heatwaves are roasting the world, smashing records with unrelenting severity. A CUHK research team has developed a high-performance radiative cooling paint based on recycled glass, a forgotten resource in our communities. It can potentially provide buildings with supplemental cooling without consuming energy.

One of the most innovative universities in the city and the region, CUHK is committed to producing impactful research and propelling innovation in Hong Kong and beyond. Recently, CUHK students and scholars have excelled in several national and international competitions, while the CUHK Hong Kong-Shenzhen Innovation and Technology Research Institute (Futian) (FITRI) has recently been unveiled to foster cross-border I&T collaboration.

Venom may be one of Spider-Man’s greatest nemeses, but the alien symbiote who can stretch and deform itself has inspired scientists to create soft robots that could transform numerous aspects of medical care, from targeted drug delivery to minimally invasive surgery. Professor Zhang Li from CUHK decided to channel Venom’s superpowers into building soft robots based on ferrofluids and a new silicone elastomer, which can be deformed in ever more complex ways, making them capable of a growing range of functions within the human body.
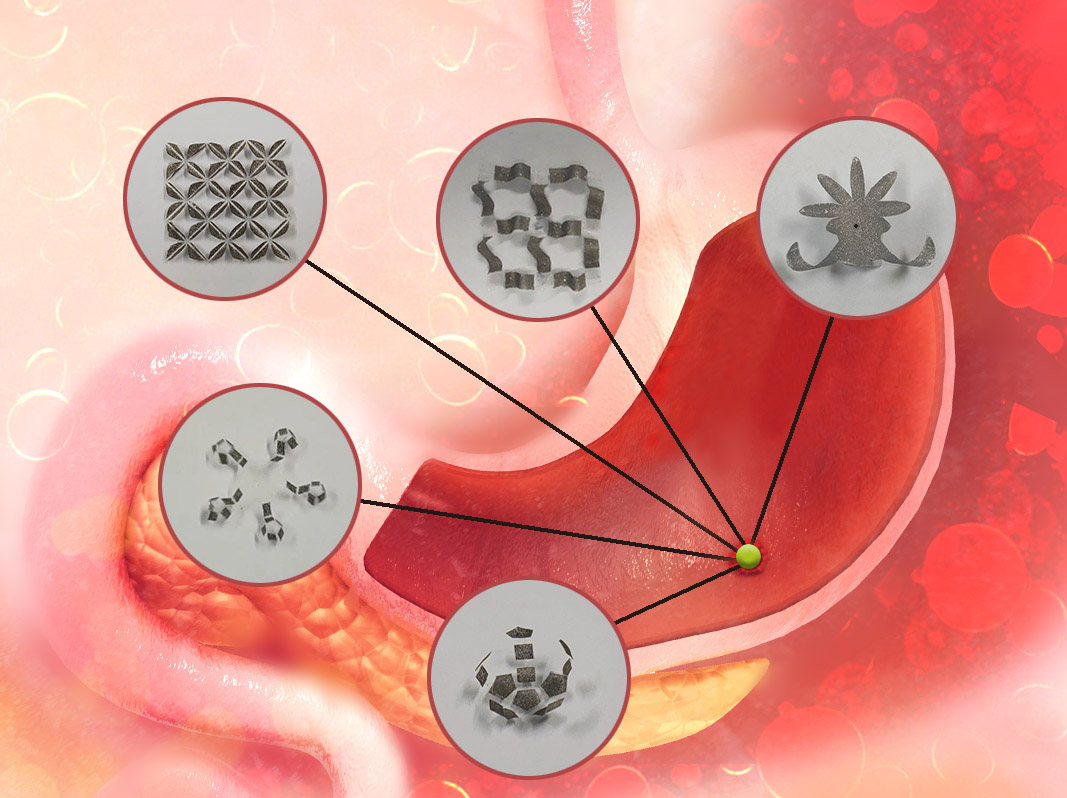
What can you do with tape? Seal your package or to bind an injury? The uses of tape go much further than that in the hands of a CUHK Engineering professor who has devoted himself to medical robotics. By simply tattooing magnetised patterns onto tapes and using a magnetic field, a highly versatile “origami” soft robot is miraculously brought into being that can morph into a variety of 3D shapes - and behold, they have a future in medical and industrial applications.
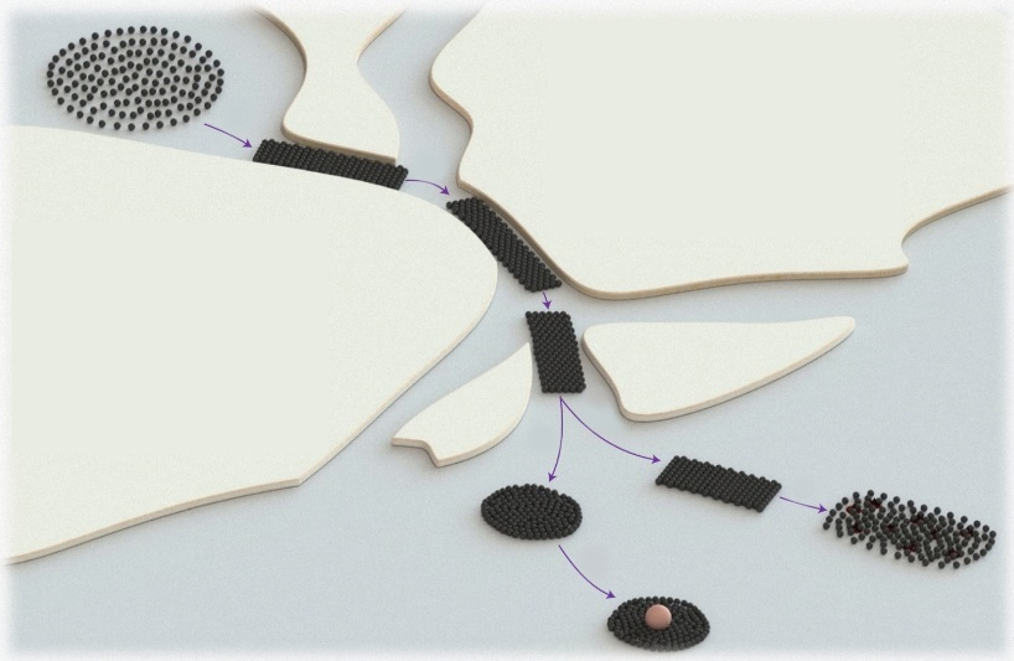
In a flower garden, we have army of honeybees that swarm to defend enemies; in a tortuous human lumen, we have army of microrobots that swarm to carry drugs that attack maladies. CUHK engineering professors have devised an avant-garde AI system that lets these microrobots navigate like bees and change shape inside complex environments like human bodies.

Life in an extremely cold region without electricity for heating and lighting can be a miserable experience, especially as existing battery technologies cannot retain a reliable power supply in such cold weather. When winter storms sweep across cities, the power crisis they cause can leave millions of people without electricity. CUHK researchers are trying to fix that with a new technology that promises to bring stability to electrical storage, even at very low temperatures.
Professor Mei-Po KWAN from CUHK’s Department of Geography and Resource Management has been awarded the James R. Anderson Medal of Honor in Applied Geography, the highest honour in the field, for her multidisciplinary contributions to applied geography; while Professor YU Jun from the Faculty of Medicine has been awarded the Guanghua Engineering Science and Technology Award by the Chinese Academy of Engineering in recognition of her distinguished achievements in gastrointestinal cancer studies.

loT is the key to building a smart city, in which sensors act as eyes and ears of the system to collect and convert physical variables into electronic signals for analysis. A self-powered wireless sensing e-sticker, thin as two human hairs, developed by CUHK, converts the power of a finger touch into electromagnetic wave signals to advance the smart sensing technology. Another discovery is a TENG with high power output to better harvest mechanical and biomechanical motion.

With a clear and pronounced emphasis on promoting “Research and Innovation”, CUHK has been working diligently to bring out talents and pioneers in the industry. Recently, CUHK scholars received global and national recognition for their research excellence, among whom Professor Dennis LO from Medicine has become the first Chinese scientist to receive the Royal Medal in biological sciences.

Driving research, innovation and entrepreneurship initiatives, CUHK recently hosted two major highlighted events, CUHK Innovation Day and CUHK Entrepreneur Day, to provide its communities an exchange platform to showcase innovation and entrepreneurial achievements to industries and the public, as well as translate innovative research into practice.
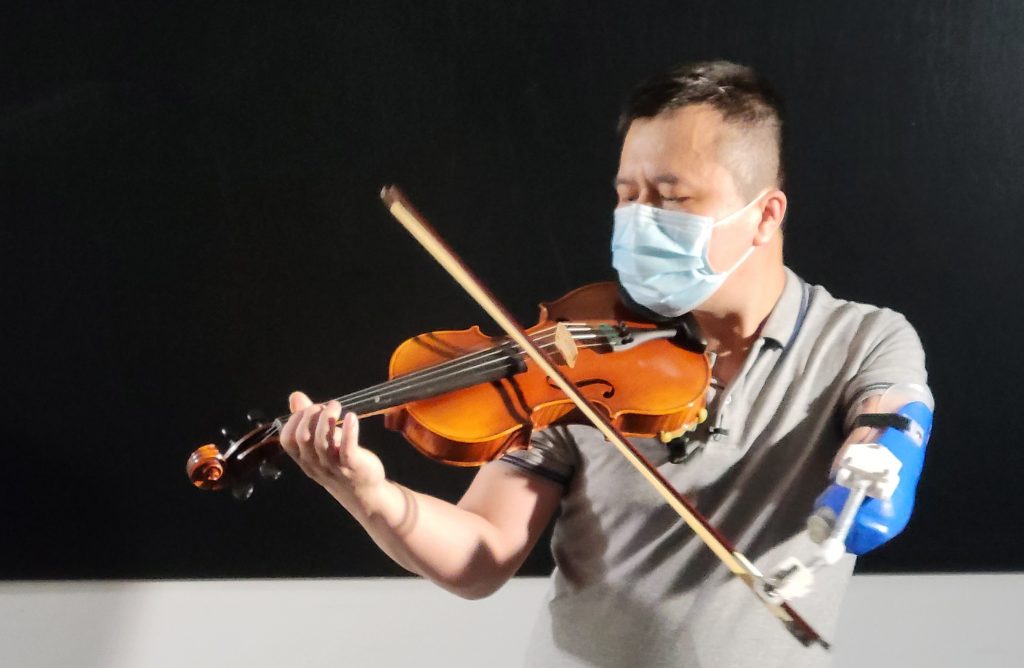
It is a tough task for an able bodied person to learn the violin, let alone someone without an arm. A multi-functional prosthetic with convertible adaptor developed by CUHK researchers gave hope to Roy who had lost his left arm and took him onto the stage in a concert given by a thousand-player orchestra, where he demonstrated his dream playing wonderful pieces of music.
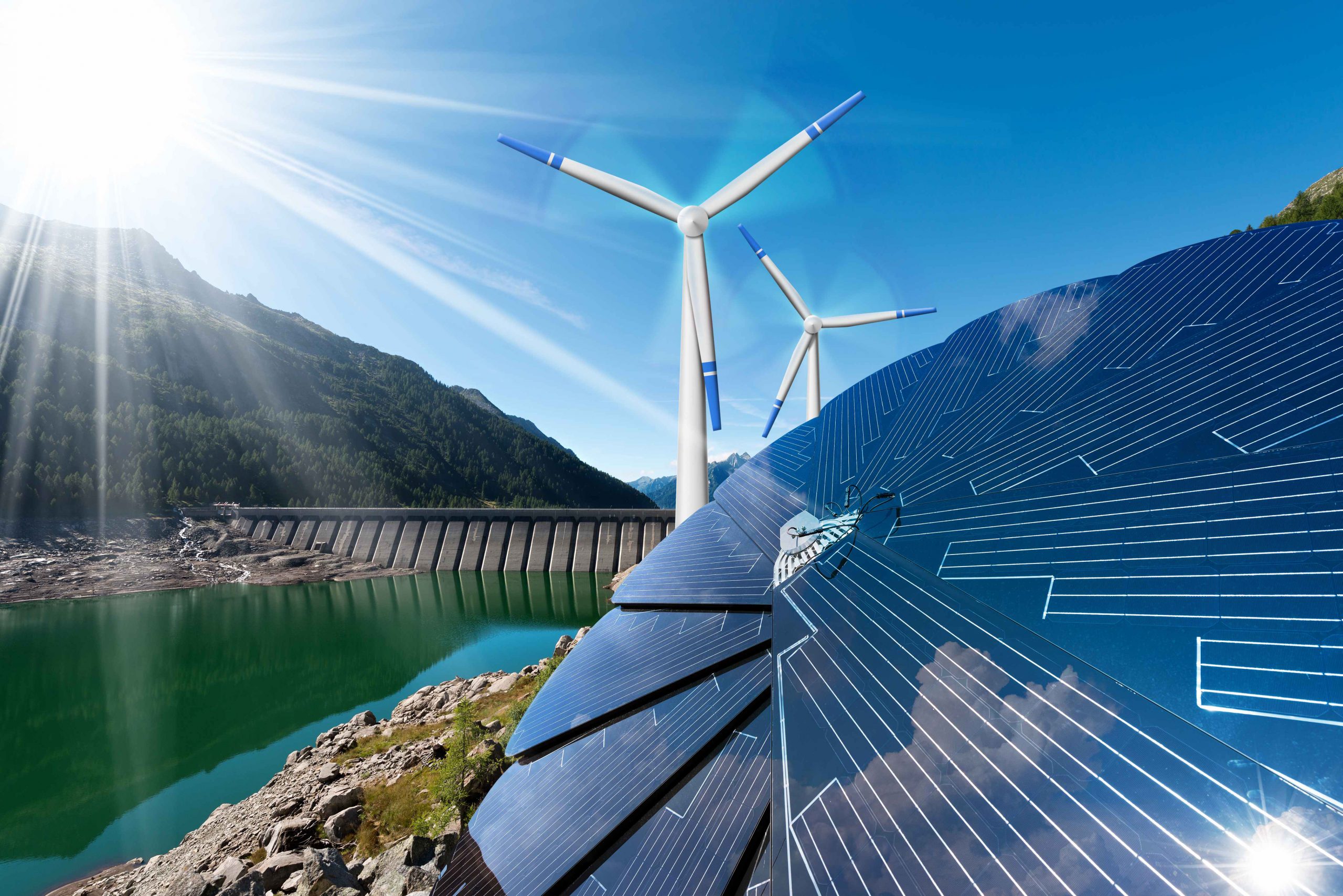

The ocean is the largest energy treasure house on earth, covering approximately 70% of its surface. Harvesting this is called “blue energy” and it’s a solution to energy crisis. However, given its complex technology and high cost, electricity generation from blue energy isn’t easy. A CUHK research team has recently developed a high-efficacy generator for harnessing ocean wave energy, which turns a new page.
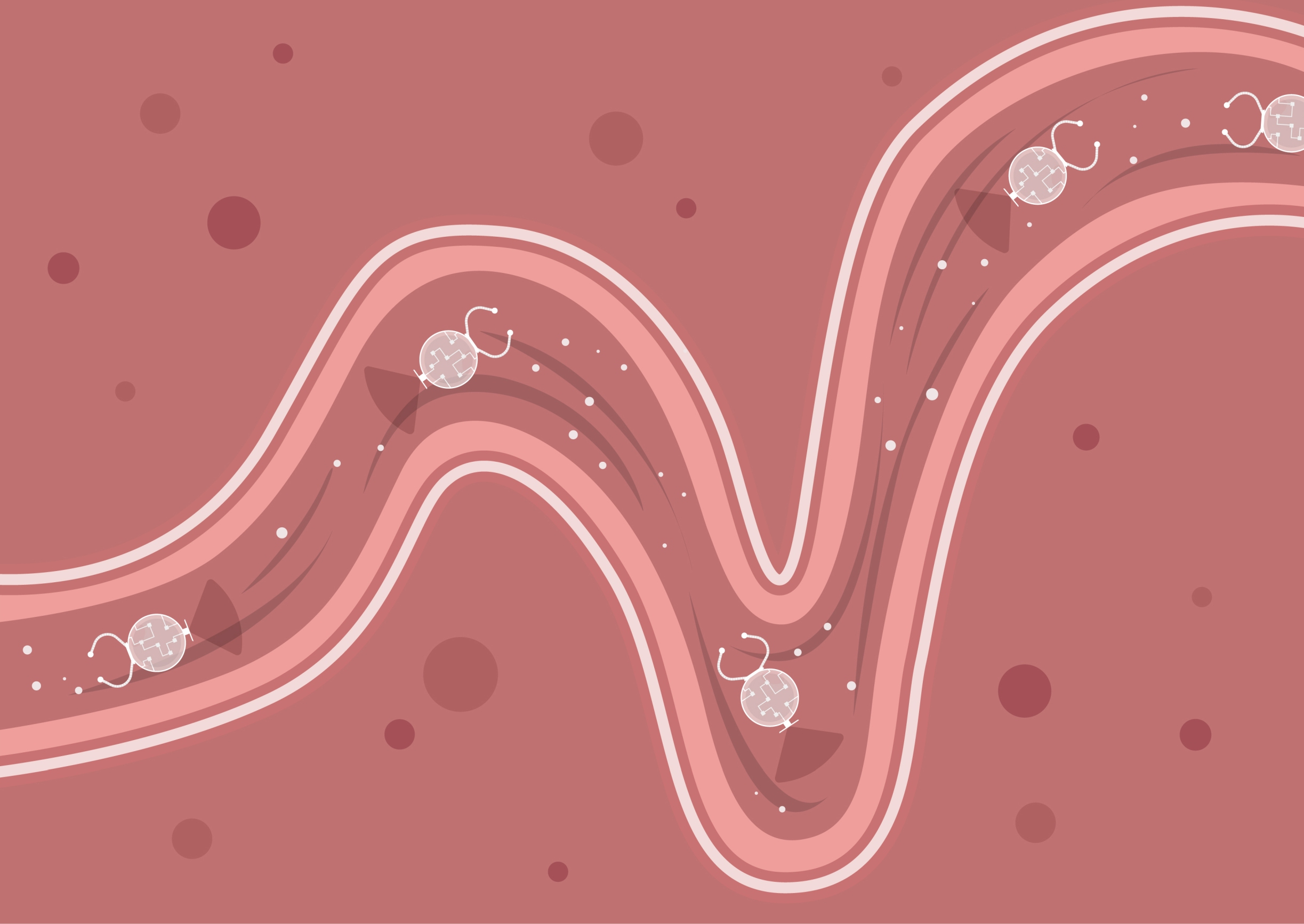
A sci-fi adventure film from the 1960s, Fantastic Voyage, features a group of doctors shrinking into microscopic size and venturing into a patient’s brain to repair damages. A CUHK research team has recently brought this surreal fantasy to life by developing biohybrid soft microrobots, which navigates in tiny lumens for health inspections and medical treatments.
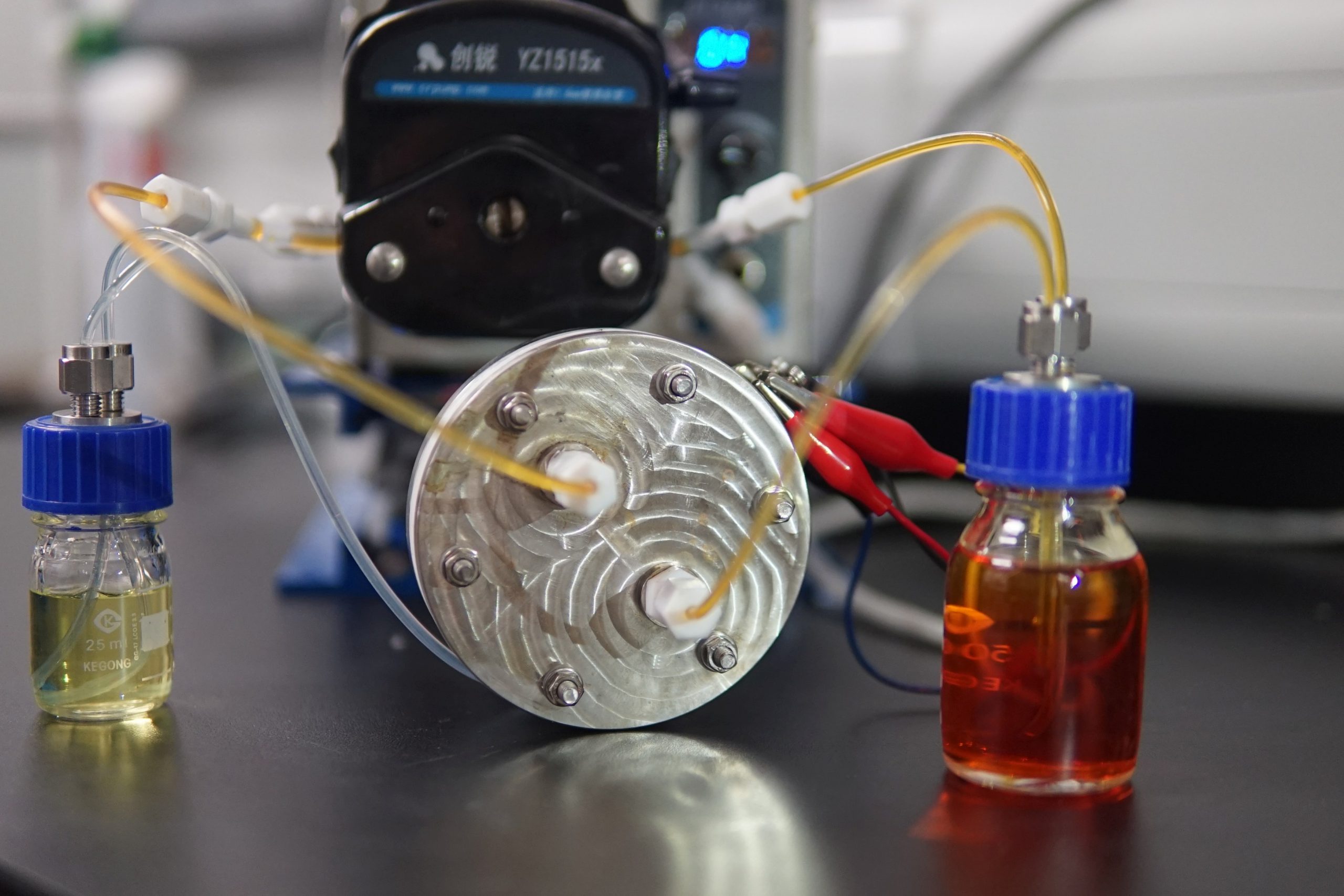
Distinguished as safe, powerful and flexible but plagued by a short life, sulphur-based redox flow batteries have been given a boost to their duration by CUHK engineers, ending a long unsolved challenge. They have designed a novel membrane, keeping the battery’s two electrodes apart and reducing the loss of active materials, so ramping up its lifetime, stability, and its usefulness in grid-scale energy storage devices.

Constant academic pursuit by scholars is essential to driving improvements in life and social progress. Scholars and research studies from CUHK have received international and national awards in various disciplines over the past few months, with research excellence widely recognised.
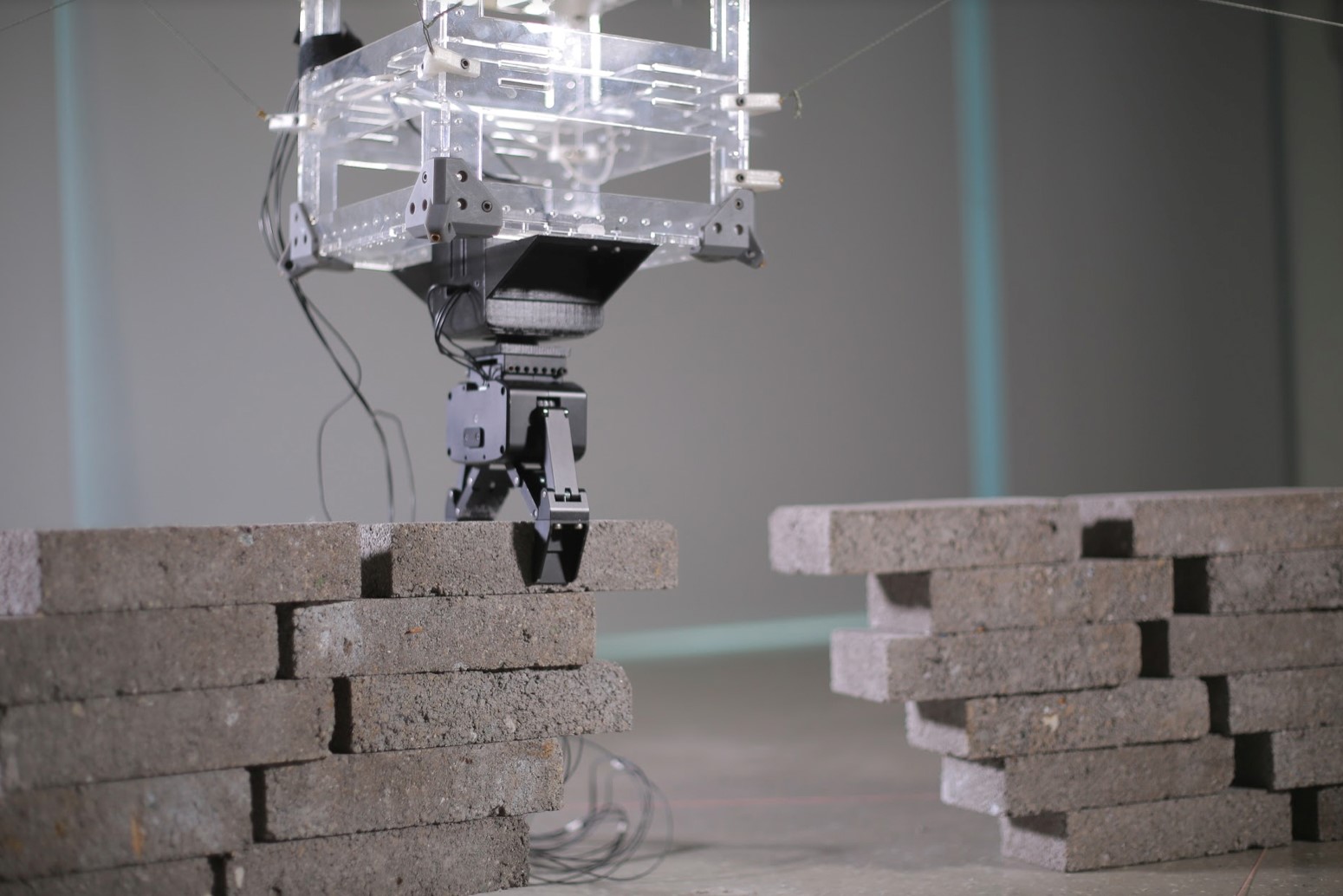

Architects always have an abundance of design ideas, yet in the real world, there are limitations such as workers’ techniques, time and building costs. A professor from CUHK shows how cable-driven robots transform non-standard and artistic designs into precise executions and eventually help realise the endless possibilities for design concepts.
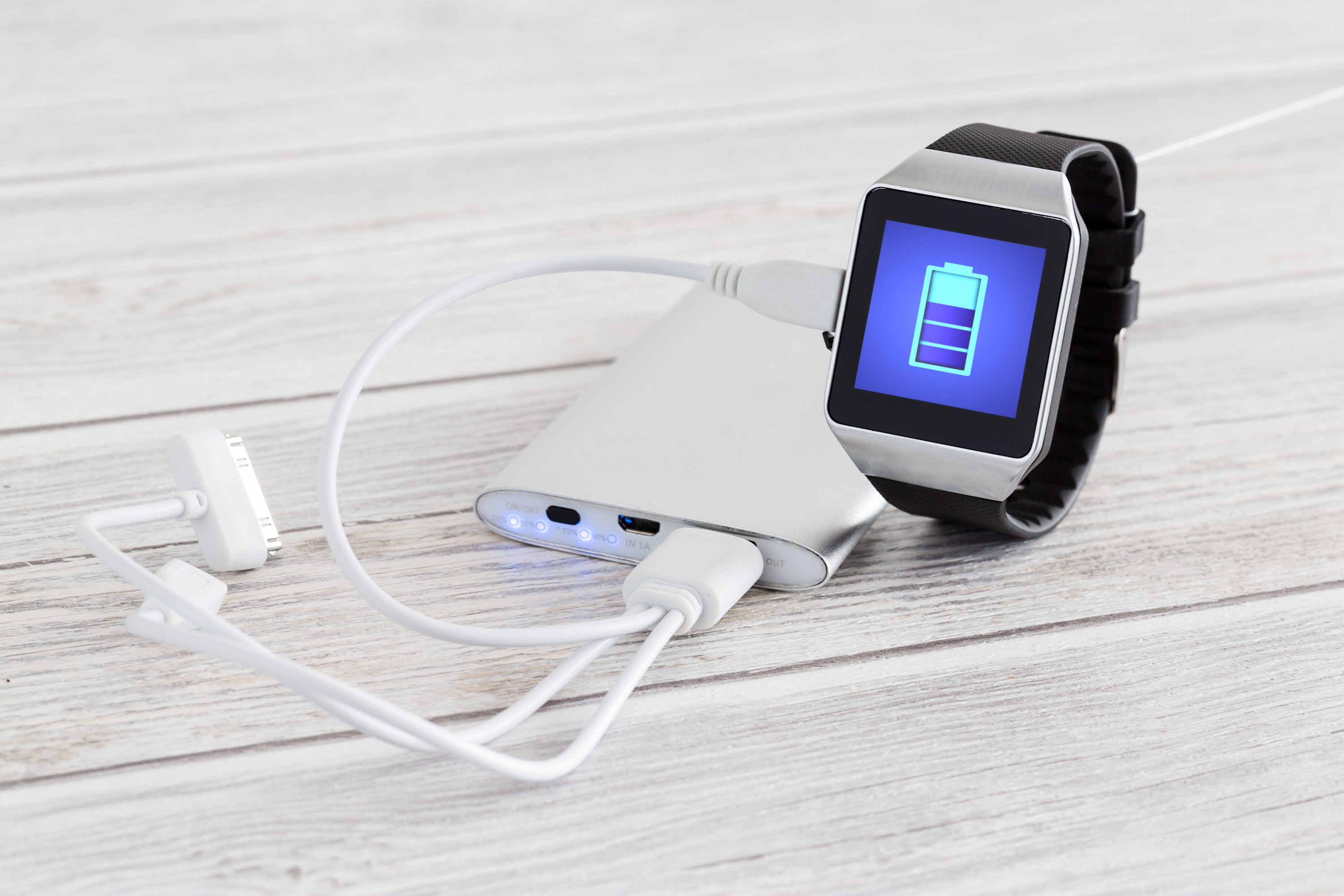

Smart wearable technology is evolving into a new form. Powering a smartwatch through solar power could be one the ways but how could it be sustainable under a lengthy cloudy sunless day? Researchers in CUHK recently found that you can be in control of your watch’s energy and sustain its battery endurance through walking and the swinging of your arms.